Notation:
m=number of training examples
n=number of features
x="input" variables / features
y="output"variable/"target" variable
((x^{(i)},y^{(i)})) = the ith trainging example
(h_theta) = fitting function
一、梯度下降法(Gradient Descent)(主要)
其中(h_theta(x)=theta_0+theta_1x_1+...+theta_nx_n=sum_{i=0}^{n}{theta_ix_i}=theta^T)
假设损失函数为(J(theta)=frac{1}{2}sum_{i=1}^{m}{(h_theta(x)-y)^2}) , To minimize the (J(theta))
main idea: Initalize (theta) (may (theta=vec{0})) ,then keep changing (theta) to reduce (J(theta)) ,untill minimum
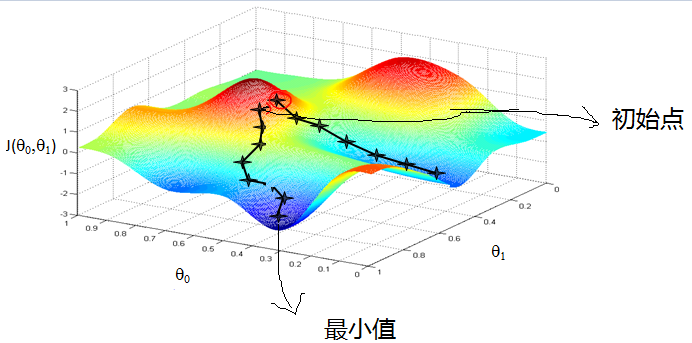
Gradient decent:
只有一个样本时,对第i个参数进行更新 (theta_i:=theta_i-alphafrac{partial }{partial theta_i}J(theta)=theta_i-alpha(h_theta(x)-y)x_i)
Repeat until convergence(收敛):
{
(theta_i:=theta_i-alphasum_{j=1}^{m}(h_theta(x^{(j)})-y^{j})x_i^{(j)}) ,(for every i)
}
矩阵描述(简单):
Repeat until convergence(收敛):
{
(theta:=theta -nabla_theta J)
}
IF (Aepsilon R^{n*n})
tr(A)=(sum_{i=1}^nA_{ii}) :A的迹
(J(theta)=frac{1}{2}(Xtheta - vec{y})^T(Xtheta - vec{y}))
(nabla_theta J=frac{1}{2}nabla_theta (theta^TX^TXtheta-theta^TX^Ty-y^Txtheta+y^Ty) =X^TXtheta-X^Ty)
备注:
当目标函数是凸函数时,梯度下降法的解才是全局最优解
二、随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent )
Repeat until convergence:
{
for j=1 to m{
(theta_i:=theta_i-alpha(h_theta(x^{(j)})-y^{j})x_i^{(j)}) ,for every i
}
}
备注:
1.训练速度很快,每次仅仅采用一个样本来迭代;
2.解可能不是最优解,仅仅用一个样本决定梯度方向;
3.不能很快收敛,迭代方向变化很大。
三、mini-batch梯度下降
Repeat until convergence:
{
for j=1 to m/n{
(theta_i:=theta_i-alphasum_{j=1}^{n}(h_theta(x^{(j)})-y^{j})x_i^{(j)}) ,for every i
}
}
备注:
机器学习中往往采用该算法
参考地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/5970503.html
文章来源: 博客园
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!




 客服
客服


