二叉树存储路径节点
1.0中虽然实现了寻路的算法,但是使用List<>来保存节点性能并不够强
寻路算法学习1.0在这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/AlphaIcarus/p/16185843.html
更好的方法是使用堆(或者叫树)来代替列表存储节点
注意:这里使用数组来实现堆,而非使用链表实现堆
这里使用二叉树的方式来存储节点之间的关系
如果在树的末尾添加了一个较小的值,
那么需要和父节点比较大小,如果更小,则交换位置
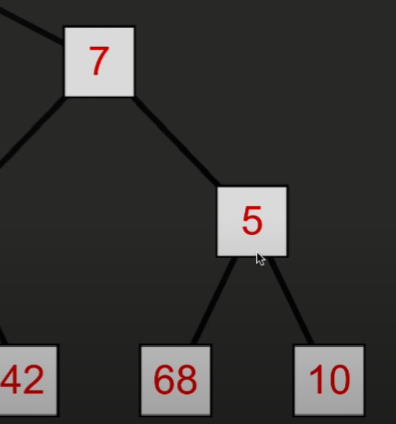
然后再与父节点比较大小,如果小于父节点,则再次交换位置

如果大于父节点,则停止交换
那如果较小的元素被移除了又怎么排序呢?(之前说过因为Clsot值比较后有时需要重新设置父节点)
首先把树末尾的节点数据添加到树顶
然后与两个子节点比较大小,和更小的那一个交换位置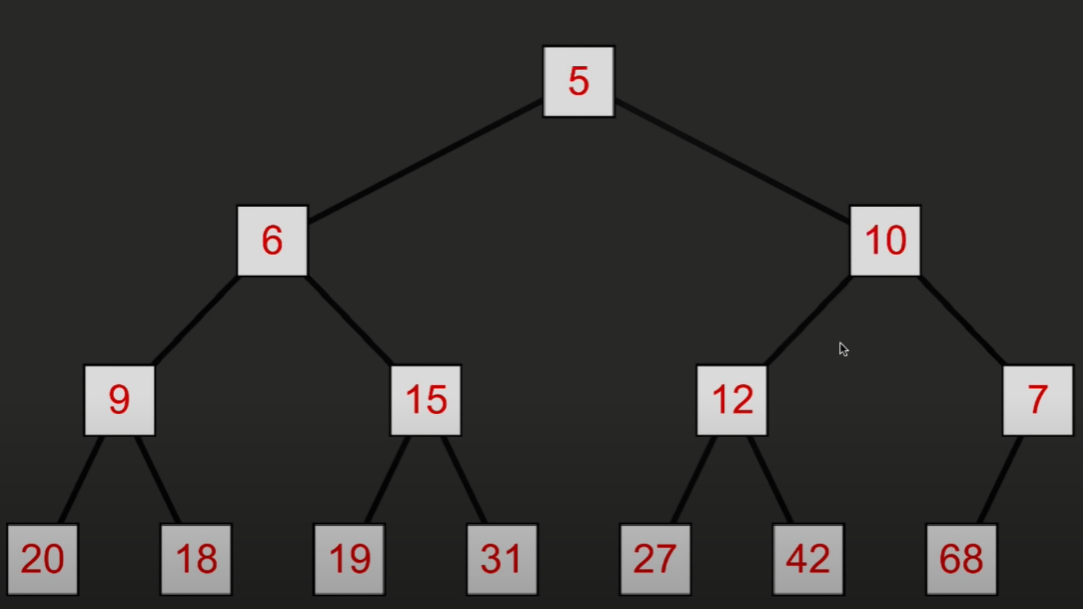
然后再与两个子节点比较大小,直到两个子节点都更大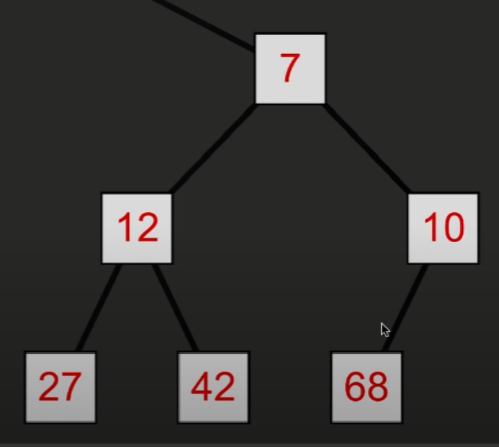
那么如何获取相关的节点呢?这里的数字表示第几个节点而不是存储的具体数据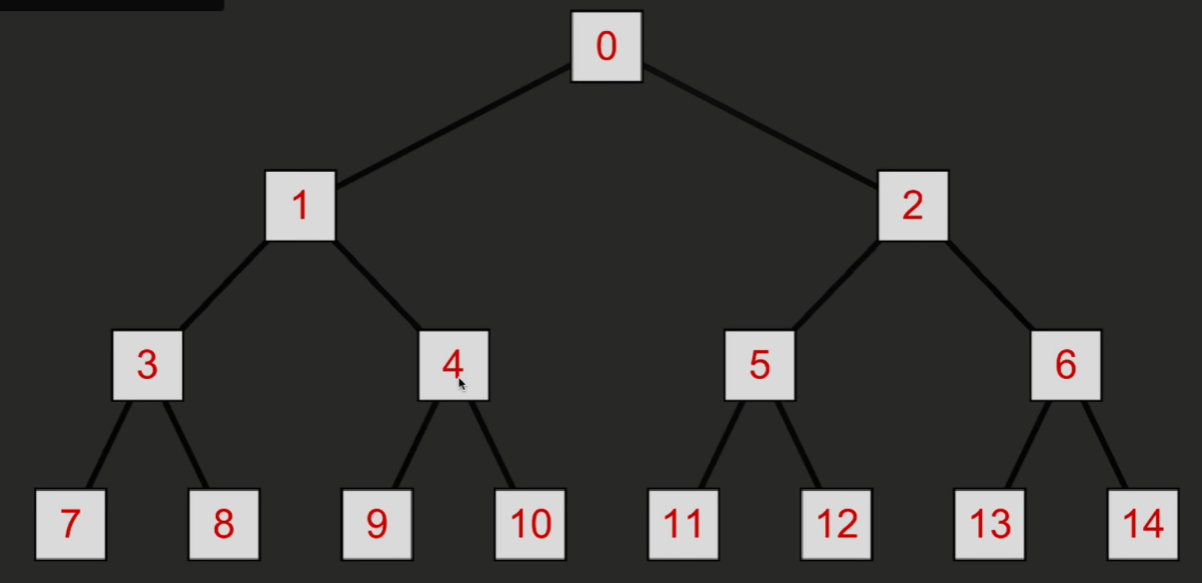
可以发现以下关系
如果获取某个节点 n (第 n 个节点)
那么该节点的父节点为 ( n - 1) / 2
左子节点为 2n + 1
右子节点为 2n + 2
在Unity中应用
新建脚本Heap,这是一个数据类型,用来代替List类型,由数组构成
public class Heap<T> where T : IHeapItem<T> //继承了该接口之后,需要实现数据类型T比较大小的方法
{
T[] items; //泛型数组,可以为任何类型的数据
int currentItemCount; //当前总共有多少元素
public int Count //属性,访问返回元素个数
{
get { return currentItemCount; }
}
public Heap(int maxHeapSize) //构造器
{
items = new T[maxHeapSize];
}
public void Add(T item) //添加新元素的方法
{
item.HeapIndex = currentItemCount;
items[currentItemCount] = item; //末尾添加新元素
SortUp(item); //排序
currentItemCount++; //元素总数+1
}
public T RemoveFirt() //获取堆顶部元素并移除
{
T firstItem = items[0]; //取得顶部元素
currentItemCount--; //元素总数-1
items[0] = items[currentItemCount]; //将最后一个元素移到顶部
items[0].HeapIndex = 0; //将该元素的索引设为0,即第一个元素
SortDown(items[0]); //下沉元素
return firstItem; //返回取得的顶部元素
}
public void UpdateItem(T item)
{
SortUp(item);
}
public bool Contains(T item) //判断是否包含元素
{
return Equals(items[item.HeapIndex], item);
}
void SortDown(T item) //下沉元素
{
while (true) //一直循环,直到值小于左右子树或到最后位置
{
int childIndexLeft = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 1; //左子树的索引
int childIndexRight = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 2; //右子树的索引
int swapIndex = 0;
if (childIndexLeft < currentItemCount) //
{
swapIndex = childIndexLeft;
if (childIndexRight < currentItemCount)
{
if (items[childIndexLeft].CompareTo(items[childIndexRight]) < 0)
{
swapIndex = childIndexRight;
}
}
if (item.CompareTo(items[swapIndex]) < 0)
{
Swap(item, items[swapIndex]);
}
else
{
return;
}
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}
private void SortUp(T item) //上浮元素
{
int parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1) / 2; //父节点的位置
while (true) //循环直至数据比父节点大
{
T parentItem = items[parentIndex];
if (item.CompareTo(parentItem) > 0) //如果新的数据比父节点更小(f值更小)
{
Swap(item, parentItem); //交换位置
}
else
{
break;
}
parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1) / 2; //下次循环前再次验证父节点索引
}
}
private void Swap(T itemA, T itemB) //交换数组中两个元素的位置
{
items[itemA.HeapIndex] = itemB;
items[itemB.HeapIndex] = itemA;
int itemAIndex = itemA.HeapIndex;
itemA.HeapIndex = itemB.HeapIndex;
itemB.HeapIndex = itemAIndex;
}
}
public interface IHeapItem<T> : IComparable<T> //接口,Heap必须实现该接口,IHeapItem继承可比较接口
{
int HeapIndex { get; set; }
}
接下来是Node
public class Node : IHeapItem<Node> //继承接口,需要实现能够比较Node大小的方法
{
......
private int heapIndex; //声明节点的索引
......
public int HeapIndex //属性
{
get { return heapIndex; }
set { heapIndex = value; }
}
public int CompareTo(Node needToCompare) //实现的比较大小的方法
{
//通过比较 F 值的大小,来判断节点的大小
int compare = FCost.CompareTo(needToCompare.FCost);
if (compare == 0)
{
compare = hCost.CompareTo(needToCompare.hCost);
}
return -compare;
}
}
接下来是PathFinding
public class PathFinding : MonoBehaviour
{
......
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
//分别注释方法,运行后比较两个方法寻找相同路径所需的时间
//FindPath(seeker.position, target.position); //之前使用List的方法
FindPathHeap(seeker.position, target.position); //新的使用Heap的方法
}
}
......
private void FindPathHeap(Vector3 startPos, Vector3 targetPos)
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); //计时器
sw.Start();
Node startNode = grid.NodeFromWorldPos(startPos); //输入空间坐标,计算出处于哪个节点位置
Node targwtNode = grid.NodeFromWorldPos(targetPos);
//这里将List替换为了Heap,初始化Heap
Heap<Node> openSet = new Heap<Node>(grid.MaxSize); //用于存储需要评估的节点
HashSet<Node> closedSet = new HashSet<Node>(); //用于存储已经评估的节点
openSet.Add(startNode);
while (openSet.Count > 0) //如果还有待评估的节点
{
Node currentNode = openSet.RemoveFirt(); //获取其中一个待评估的节点
closedSet.Add(currentNode); //将该节点加入已评估的节点,之后不再参与评估
if (currentNode == targwtNode) //如果该节点为目标终点,就计算出实际路径并结束循环
{
sw.Stop();
print("Path found: " + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
RetracePath(startNode, targwtNode);
return;
}
//如果该节点不是目标点,遍历该点周围的所有节点
foreach (Node neighbor in grid.GetNeighbors(currentNode))
{
//如果周围某节点不能行走 或 周围某节点已经评估,为上一个节点,则跳过
// 说明某节点已经设置父节点
if (!neighbor.walkable || closedSet.Contains(neighbor))
{
continue;
}
//计算前起始点前往某节点的 gCost 值,起始点的 gCost 值就是0
//经过循环这里会计算周围所有节点的g值
int newMovementCostToNeighbor = currentNode.gCost + GetDinstance(currentNode, neighbor);
//如果新路线 gCost 值更小(更近), 或 某节点没有评估过(为全新的节点)
if (newMovementCostToNeighbor < neighbor.gCost || !openSet.Contains(neighbor))
{
neighbor.gCost = newMovementCostToNeighbor; //计算某节点gCost
neighbor.hCost = GetDinstance(neighbor, targwtNode); //计算某节点hCost
neighbor.parent = currentNode; //将中间节点设为某节点的父节点
//如果存在某节点gCost更小的节点,会重新将中间节点设为某节点父节点
if (!openSet.Contains(neighbor)) //如果某节点没有评估过
{
openSet.Add(neighbor); //将某节点加入待评估列表,在下一次循环进行评估,
}
}
}
}
}
......
}
接下来是MyGrid
public class MyGrid : MonoBehaviour
{
public bool onlyPlayPathGizmos; //是否只绘制路径,便于观察
......
void Start()
{
nodeDiameter = nodeRadius * 2;
gridSizeX = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.x / nodeDiameter); //计算出x轴方向有多少个节点
gridSizeY = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.y / nodeDiameter); //计算出z轴方向有多少个节点
CreateGrid();
}
public int MaxSize //属性,返回地图路径点的数量
{
get { return gridSizeX * gridSizeY; }
}
......
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(transform.position, new Vector3(gridWorldSize.x, 1, gridWorldSize.y));
if (grid != null)
{
Node playerNode = NodeFromWorldPos(player.position);
if (onlyPlayPathGizmos)
{
//只绘制路径
if (path != null)
{
foreach (Node node in path)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawCube(node.worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - 0.1f));
}
}
}
else //绘制地图所有点和路径
{
foreach (Node node in grid)
{
......
}
}
}
}
}
接下来为了体现两个方法的耗时差距
修改一下地图的大小和节点的大小
运行结果:

使用Heap的耗时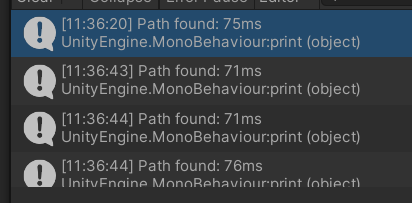
使用List的耗时
可以看见速度大概提高了三倍
内容来源于网络如有侵权请私信删除
文章来源: 博客园
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!


 客服
客服


