什么是TCP代理
TCP代理是一种网络代理技术,它允许客户端和服务器之间通过一个位于中间的第三方TCP代理服务器进行通信。TCP代理的工作方式是客户端向代理服务器发送TCP连接请求,代理服务器将此请求转发到目标服务器,然后等待目标服务器响应。当目标服务器响应时,代理服务器将响应转发回客户端。
整体功能规划
(1)显示本地设备与远程设备之间的通信过程
(2)处理代理两端发送和接收的数据
(3)创建和管理socket
打印设备之间的通信过程
# 所有可打印字符(长度为3)保持不变,不可打印字符改为句点“.”表示
# chr函数用于将i转换为相应的ASCII字符
# repr函数返回一个对象的字符串表示形式,通常用于调试和打印目的。对于大多数字符,repr(chr(i))返回一个长度为 3 的字符串,其中第一个和最后一个字符是单引号(')或双引号("),中间的字符是该字符本身
HEX_FILTER = ''.join([(len(repr(chr(i))) == 3) and chr(i) or '.' for i in range(256)])
# hexdump函数能接收bytes或string类型的输入,并将其转换为十六进制格式输出到屏幕上
# 它能同时以十六进制数和ASCII可打印字符的格式,输出数据包的详细内容。
# 这有助于理解未知协议的格式,或是在明文协议里查找用户的身份凭证等
def hexdump(src, length=16, show=True):
# 如果传进来的参数是bytes类型,调用decode函数将它转换为string类型
if isinstance(src, bytes):
src = src.decode()
results = list()
for i in range(0, len(src), length):
# 从src中取出一段数据放入word变量
word = str(src[i : i + length])
# 调用内置的translate函数把整段数据转换成可打印字符的格式,保存到printable变量里,HEX_FILTER为翻译表
printable = word.translate(HEX_FILTER)
# 将word中的数据转换为十六进制保存在变量hexa中
hexa = ' '.join([f'{ord(c):02x}' for c in word])
hexwidth = length * 3
# 将word变量起始点的偏移、其十六进制表示和可打印字符表示形式打包成一行字符串,放入results数组
results.append(f'{i : 04x} {hexa:<{hexwidth}} {printable}')
if show:
for line in results:
print(line)
else:
return results
处理代理两端发送和接收的数据
# 从代理两端接收数据
def receive_from(connection):
# 用来存储socket对象返回的数据
buffer = b""
connection.settimeout(5)
try:
# 创建一个循环,不断把返回的数据写进buffer,直到数据读完或者连接超时为止。最后,把buffer返回给调用方.
while True:
data = connection.recv(4096)
if not data:
break
buffer += data
except Exception as e:
pass
return buffer
def request_handler(buffer):
# 此处可添加修改请求包操作
return buffer
def response_handler(buffer):
# 此处可添加修改返回包操作
return buffer
def proxy_handler(client_socket, remote_host, remote_port, receive_first):
# 连接远程主机
remote_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
remote_socket.connect((remote_host, remote_port))
# 进入主循环之前,先确认是否需要先从远端设备接收数据
if receive_first:
remote_buffer = receive_from(remote_socket)
hexdump(remote_buffer)
remote_buffer = response_handler(remote_buffer)
if len(remote_buffer):
print("[<==] sending %d bytes to localhost." % len(remote_buffer))
client_socket.send(remote_buffer)
while True:
# 从本地客户端读取数据,打印本地数据,处理请求数据,转发给远程服务器
local_buffer = receive_from(client_socket)
if len(local_buffer):
line = "[==>]Received %d bytes from localhost." % len(local_buffer)
print(line)
hexdump(local_buffer)
local_buffer = request_handler(local_buffer)
remote_socket.send(local_buffer)
print("[==>] Sent to remote.")
# 从远程服务器读取数据,打印远端数据,处理响应数据,转发给本地客户端
remote_buffer = receive_from(remote_socket)
if len(remote_buffer):
print("[<==]Received %d bytes from remote." % len(remote_socket))
hexdump(local_buffer)
remote_buffer = request_handler(remote_buffer)
client_socket.send(remote_buffer)
print("[<==] Sent to localhost.")
# 当通信两端都没有任何数据时关闭两端的socket,退出代理循环
if not len(local_buffer) or not len(remote_buffer):
client_socket.close()
remote_socket.close()
print("[*]No more data. closing connections.")
break
创建和管理socket
def server_loop(local_host, local_port, remote_host, remote_port, receive_first):
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 创建一个socket并绑定到本地端口开始监听
try:
server.bind((local_host, local_port))
except Exception as e:
print(" problem on bind: %r" % e)
print("[!!] Failed to listen on %s:%d" % (local_host, local_port))
print("[!!] check for other listening sockets or correct permissions. ")
sys.exit(e)
print("[*] Listening on %s: %d" % (local_host, local_port))
server.listen(5)
# 每出现一个新连接就新开一个线程,将新连接交给proxy_handler函数
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
line = "> Received incoming connection from %s:%d" % (addr[0], addr[1])
print(line)
proxy_thread = threading.Thread(
target=proxy_handler,
args=(client_socket, remote_host, remote_port, receive_first)
)
proxy_thread.start()
整体代码
完整代码可以参考我的Github仓库:Github
代码测试
这里使用kali虚拟机(192.168.131.135)作为本地机器,使用ubuntu虚拟机(192.168.131.132)作为TCP代理机器和FTP服务器。
首先在ubuntu上运行该代码: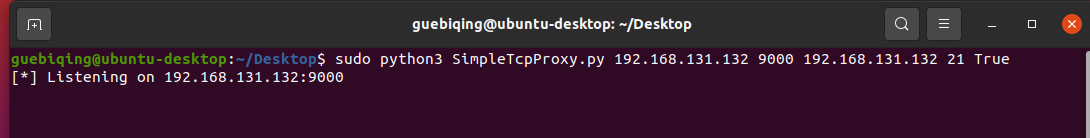
接着,在本地kali机器上连接ubuntu的9000端口进行登录: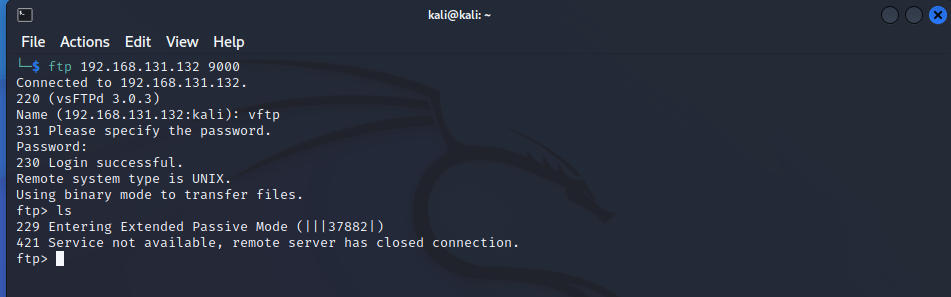
此时可以看到ubuntu机器上已经打印出了数据:
内容来源于网络如有侵权请私信删除
文章来源: 博客园
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!




 客服
客服


