题目描述

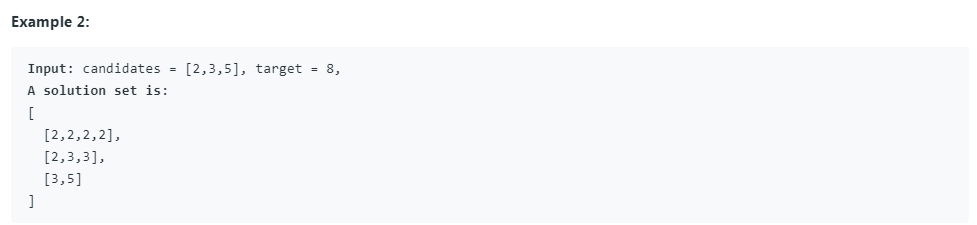
给定一个无重复的正整数数组 candidates 和一个正整数 target, 求所有和为 target 的 candidates 中数的组合中。其中相同数的不同顺序组合算做同一种组合,candidates 中的数可以重复使用。
算法一
首先想到的方法就是枚举所有的组合可能性,判断其和是否为target。枚举的方法可以使用递归,对candidates中每一个数,有“加入组合”和“不加入组合”两种选择,每一种选择又可以向后面元素的不同选择递归,直到candidate中最后一个元素。可以用剪枝来减少算法的运行时间,如果当前组合的和大于target,则当前情形下已不会有合适的组合了。
AC代码如下:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); dfs(candidates, 0, target, new ArrayList<Integer>(), res); return res; } private void dfs(int[] candidates, int index, int target, List<Integer> combination, List<List<Integer>> res) { if(target < 0) return; if(target == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(combination)); return; } for(int i=index; i<candidates.length; i++) { if(candidates[i] > target) continue; //选择当前元素 combination.add(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i, target - candidates[i], combination, res); //不选择当前元素 combination.remove(combination.size() - 1); } } }
算法二
本题符合动态规划的思想,用一个map记录不同target的全部组合,target <= 0的组合为空, target = i的组合为全部 target = i - candidates[j] (0<j<candidates.length)的组合加上candidates[j]。
这里需要注意,因为题目要求相同元素的不同顺序算同一种组合方式,上诉方法会出现[2,3,2] 和 [2,2,3]这样两种组合方式。可以用将每一种组合排序后加入set的方法来去重。
AC代码:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { Map<Integer, List<List<Integer>>> dp = new HashMap<Integer, List<List<Integer>>>(); return dp(target, 0, candidates, dp); } private List<List<Integer>> dp(int target, int index, int[] candidates, Map<Integer, List<List<Integer>>> map){ if(map.containsKey(target)) { return map.get(target); } List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<>(); Set<List<Integer>> resSet = new HashSet<>(); //这里一定要能够区分出 小于0和等于0. 等于0时加一个空的,避免出现[2,3,6,7] ,target = 7时,6被放入其中!!!! if(target < 0 ) return resList; if(target == 0){ resList.add(new ArrayList<>()); return resList; } for(int i=index; i<candidates.length; i++){ List<List<Integer>> subResList = dp(target - candidates[i], index, candidates, map); if(subResList.size() > 0) { for(List<Integer> subRes : subResList) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(subRes); res.add(candidates[i]); Collections.sort(res); resSet.add(res); } } } for(List<Integer> l : resSet) { resList.add(l); } map.put(target, resList); return resList; } }
算法三
本题还可以采用背包问题的思想,target相当于背包的容量,candidates为物品。
用一个map记录sum的范围从0~target的所有组合,容量为 i 的组合求解方式如下:遍历每一个物品candidates[j], 获取容量为 i - candidates[j]的所有组合,加入该物品。
这里值得注意的是,因为题目要求相同元素的不同顺序算同一种组合方式,因此需要将物品的循环放在容量循环的外面,这样就可以避免出现重复出现[2,3,2] 和 [2,2,3]这样两种组合方式。
AC代码:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { Map<Integer, List<List<Integer>>> m = new HashMap<>(); m.put(0, new ArrayList<List<Integer>>()); for(int i=0; i<candidates.length; i++){ for(int j=0; j<=target; j++){ if(j < candidates[i]) continue; List<List<Integer>> l = m.get(j - candidates[i]); if(l != null) { List<List<Integer>> jList = m.getOrDefault(j, new ArrayList<List<Integer>>()); if(l.size() == 0){ List<Integer> lcurr = new ArrayList<>(); lcurr.add(candidates[i]); jList.add(lcurr); }else{ for(List<Integer> listInL : l){ List<Integer> lcurr = new ArrayList<>(listInL); lcurr.add(candidates[i]); jList.add(lcurr); } } m.put(j, jList); } } } return m.getOrDefault(target, new ArrayList<List<Integer>>()); } }
内容来源于网络如有侵权请私信删除
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!




 客服
客服


