Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree (M)
题目
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
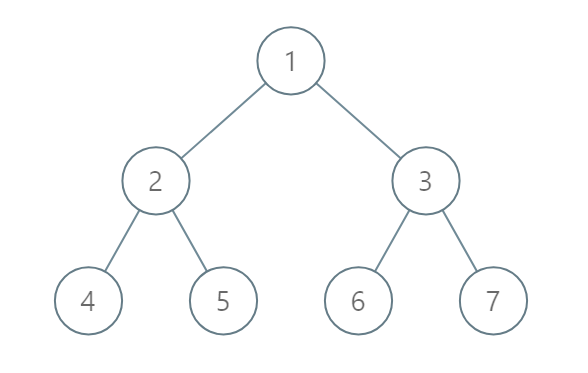
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
题意
定义二叉树中一个结点的横坐标为x,纵坐标为y,则其左子结点坐标为(x-1, y-1),其右子结点坐标为(x+1, y-1),求该二叉树的纵向遍历,类似于层序遍历,x相同的结点属于同一层,不同层按x升序排列,同一层结点按y降序排列。
思路
层序遍历所有结点,这样可以保证y值是递减的;结点的x轴信息可以用一个与层序遍历同步的队列来记录;最终结果可以用一个(x->List)的map保存。注意同一层x值相同的两个结点需要按照值大小排列,因此每一层可以再开一个map进行处理,再合并到结果map中。
代码实现
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> hash = new TreeMap<>();
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> tmp = new HashMap<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> coord = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
q.offer(root);
coord.offer(0);
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
tmp.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
int x = coord.poll();
tmp.putIfAbsent(x, new TreeSet<>());
tmp.get(x).add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
q.offer(cur.left);
coord.offer(x - 1);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.offer(cur.right);
coord.offer(x + 1);
}
}
for (int x : tmp.keySet()) {
hash.putIfAbsent(x, new ArrayList());
hash.get(x).addAll(tmp.get(x));
}
}
for (List<Integer> list : hash.values()) {
ans.add(list);
}
return ans;
}
}
文章来源: 博客园
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!




 客服
客服


