1.自定义枚举类
public enum ReturnCode {
RC200(200, "ok"),
RC400(400, "请求失败,参数错误,请检查后重试。"),
RC404(404, "未找到您请求的资源。"),
RC405(405, "请求方式错误,请检查后重试。"),
RC500(500, "操作失败,服务器繁忙或服务器错误,请稍后再试。");
// 自定义状态码
private final int code;
// 自定义描述
private final String msg;
ReturnCode(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}
该枚举类为我们和前端约定好的返回状态码和描述信息,可根据自己的需求修改状态码和描述
2.自定义统一返回格式类
@Data
public class R<T> {
private Integer code; //状态码
private String msg; //提示信息
private T data; //数据
private long timestamp;//接口请求时间
public R() {
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static <T> R<T> success(T data) {
R<T> r = new R<>();
r.setCode(ReturnCode.RC200.getCode());
r.setMsg(ReturnCode.RC200.getMsg());
r.setData(data);
return r;
}
public static <T> R<T> error(int code, String msg) {
R<T> r = new R<>();
r.setCode(code);
r.setMsg(msg);
r.setData(null);
return r;
}
}
@Data注解为Lombok工具类库中的注解,提供类的get、set、equals、hashCode、canEqual、toString方法,使用时需配置Lombok,如不配置请手动生成相关方法。
我们返回的信息至少包括code、msg、data三部分,其中code是我们后端和前端约定好的状态码,msg为提示信息,data为返回的具体数据,没有返回数据则为null。除了这三部分外,你还可以定义一些其他字段,比如请求时间timestamp。
定义了统一返回类后,controller层返回数据时统一使用R.success()方法封装。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test1")
public R<List<Student>> getStudent() {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setId(1);
student1.setName("name1");
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setId(2);
student2.setName("name2");
list.add(student1);
list.add(student2);
return R.success(list);
}
}
@Data
class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
例如在以上代码中,我们的需求是查询学生信息,我们调用这个test1接口就返回了以下的结果:
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "ok",
"data": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "name1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "name2"
}
],
"timestamp": 1692805971309
}
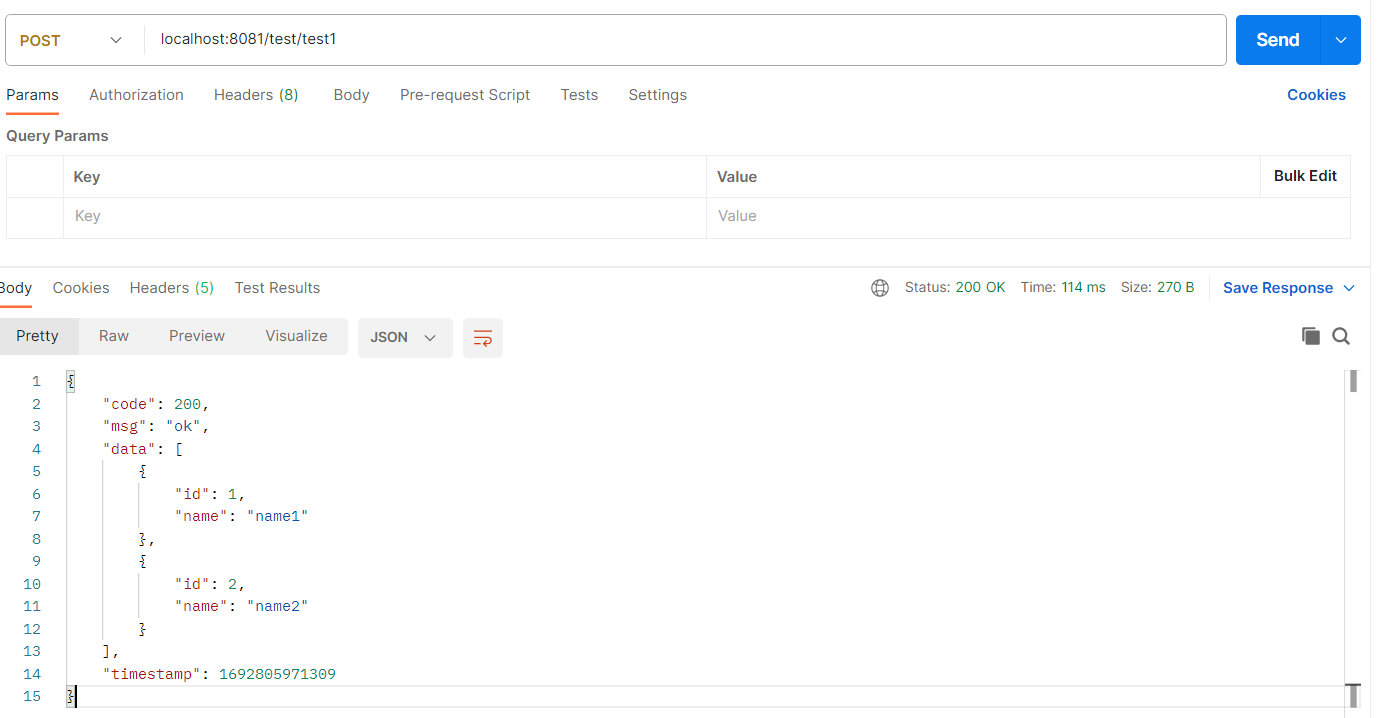
到这里我们已经基本实现了统一返回格式,但是上面这种实现方式也有一个缺点,就是每次返回数据的时候都需要调用R.success()方法,非常麻烦,我们希望能够在controller层里直接返回我们实际的数据,即data字段中的内容,然后自动帮我们封装到R.success()之中,因此我们需要一种更高级的方法。
3.统一返回格式的高级实现
我们需要利用springboot的ResponseBodyAdvice类来实现这个功能,ResponseBodyAdvice的作用:拦截Controller方法的返回值,统一处理返回值/响应体
/**
* 拦截controller返回值,封装后统一返回格式
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ResponseAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice<Object> {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class converterType) {
return true;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object o, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
//如果Controller返回String的话,SpringBoot不会帮我们自动封装而直接返回,因此我们需要手动转换成json。
if (o instanceof String) {
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(R.success(o));
}
//如果返回的结果是R对象,即已经封装好的,直接返回即可。
//如果不进行这个判断,后面进行全局异常处理时会出现错误
if (o instanceof R) {
return o;
}
return R.success(o);
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice是@RestController注解的增强,可以实现三个方面的功能:
- 全局异常处理
- 全局数据绑定
- 全局数据预处理
经过上面的处理后,我们就不需要在controller层使用R.success()进行封装了,直接返回原始数据,springboot就会帮我们自动封装。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test1")
public List<Student> getStudent() {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setId(1);
student1.setName("name1");
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setId(2);
student2.setName("name2");
list.add(student1);
list.add(student2);
return list;
}
}
@Data
class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
此时我们调用接口返回的数据依然是自定义统一返回格式的json数据
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "ok",
"data": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "name1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "name2"
}
],
"timestamp": 1692805971325
}
需要注意的是,即使我们controller层的接口返回类型是void,ResponseBodyAdvice类依然会帮我们自动封装,其中data字段为null。返回的格式如下:
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "ok",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692805971336
}
4.全局异常处理
如果我们不做统一异常处理,当后端出现异常时,返回的数据就变成了下面这样:
后端接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test1")
public String getStudent() {
int i = 1/0;
return "hello";
}
}
返回json:
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "ok",
"data": {
"timestamp": "2023-08-23T16:13:57.818+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"path": "/test/test1"
},
"timestamp": 1692807237832
}
code返回了200,又在data中显示500错误,这显然不是我们想要的结果,我们想要的结果应该时code返回500,data返回null。解决的方式有很多,你可以通过try catch的方式来捕获,但是我们并不知道什么时候会出现异常,而且手动写try catch并不方便。因此我们需要进行全局异常处理 。
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class RestExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理异常
*
* @param e otherException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public R<String> exception(Exception e) {
log.error("异常 exception = {}", e.getMessage(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC500.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC500.getMsg());
}
}
说明:
@RestControllerAdvice,RestController的增强类,可用于实现全局异常处理器@ExceptionHandler,统一处理某一类异常,比如要获取空指针异常可以@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
除此之外,你还可以使用@ResponseStatus来指定客户端收到的http状态码,如@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)则客户端收到的http状态码为500。如果不指定,则默认返回200。在这里我们并没有指定,因此我们的请求返回的http状态码全部是200,当出现异常时,我们可以修改统一返回格式中code的状态码,来表明具体情况。
具体效果如下:
接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test1")
public void test() {
int i = 1/0; //发生除0异常
}
}
返回json:
{
"code": 500,
"msg": "操作失败,服务器繁忙或服务器错误,请稍后再试。",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692808061062
}
基本上实现了我们的需求。
5.更优雅的全局异常处理
在上面的全局异常处理中,我们直接捕获了Exception.class,无论什么异常都统一处理,但实际上我们需要根据不同的异常进行不同的处理,如空指针异常可能是前端传参错误,以及我们的自定义异常等。
自定义异常如下:
@Getter
@Setter
public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {
private int code;
private String msg;
public BusinessException() {
}
public BusinessException(ReturnCode returnCode) {
this(returnCode.getCode(),returnCode.getMsg());
}
public BusinessException(int code, String msg) {
super(msg);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
}
注:@Getter和@Setter分别提供了get和set方法,同样需要Lombok依赖。
我们在全局异常处理中可以使用@ExceptionHandler指定异常类型,分别处理不同的异常
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class RestExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理自定义异常
*
* @param e BusinessException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public R<String> businessException(BusinessException e) {
log.error("业务异常 code={}, BusinessException = {}", e.getCode(), e.getMessage(), e);
return R.error(e.getCode(), e.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理空指针的异常
*
* @param e NullPointerException
* @return
* @description 空指针异常定义为前端传参错误,返回400
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public R<String> nullPointerException(NullPointerException e) {
log.error("空指针异常 NullPointerException ", e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC400.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC400.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理其他异常
*
* @param e otherException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public R<String> exception(Exception e) {
log.error("未知异常 exception = {}", e.getMessage(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC500.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC500.getMsg());
}
}
需要注意的是一个异常只会被捕获一次,比如空指针异常,只会被第二个方法捕获,处理之后不会再被最后一个方法捕获。当上面两个方法都没有捕获到指定异常时,最后一个方法指定了@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)就可以捕获到所有的异常,相当于if elseif else语句
分别测试自定义异常、空指针异常以及其他异常:
-
自定义异常
接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test1")
public void test() {
throw new BusinessException(ReturnCode.RC500.getCode(),"发生异常");
}
}
返回json:
{
"code": 500,
"msg": "发生异常",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692809118244
}
-
空指针异常:
接口:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @PostMapping("/test1") public void test(int id, String name) { System.out.println(id + name); boolean equals = name.equals("11"); } }请求:
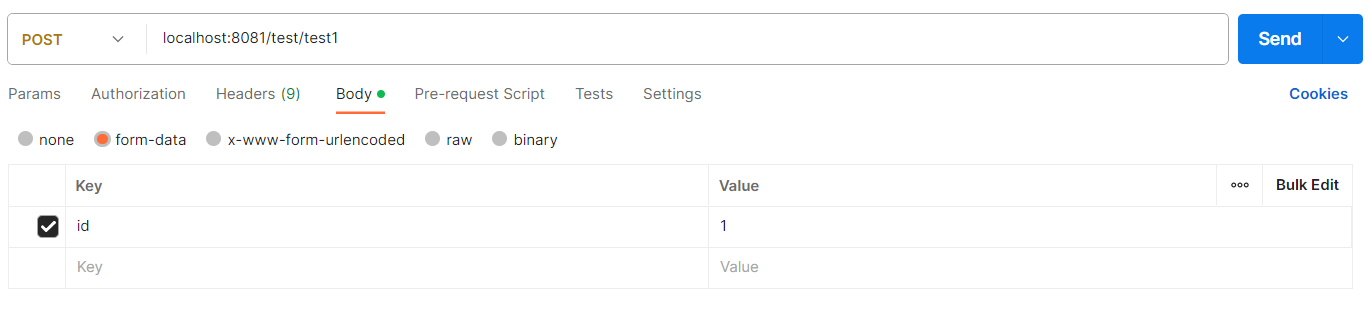
返回json:
{ "code": 400, "msg": "请求失败,参数错误,请检查后重试。", "data": null, "timestamp": 1692809456917 } -
其他异常:
接口:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @PostMapping("/test1") public void test() { throw new RuntimeException("发生异常"); } }返回json:
{ "code": 500, "msg": "操作失败,服务器繁忙或服务器错误,请稍后再试。", "data": null, "timestamp": 1692809730234 }
6.处理404错误
即使我们配置了全局异常处理,当出现404 not found等4xx错误时,依然会出现意外情况:
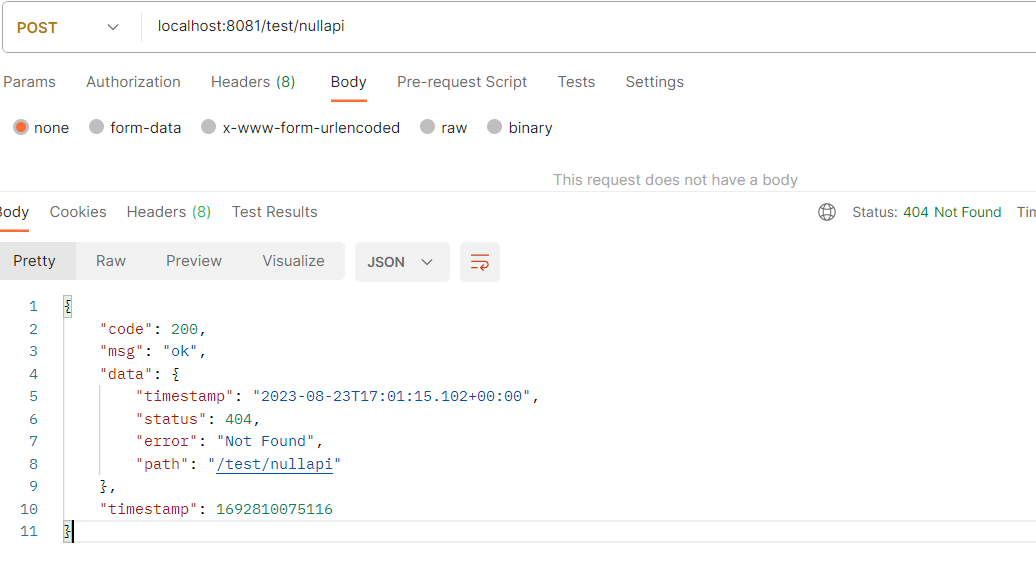
返回json:
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "ok",
"data": {
"timestamp": "2023-08-23T17:01:15.102+00:00",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"path": "/test/nullapi"
},
"timestamp": 1692810075116
}
我们可以看到发生404错误时控制台并没有报异常,原因是404错误并不属于异常,全局异常处理自然不会去捕获并处理。因此我们的解决方法是当出现4xx错误时,让springboot直接报异常,这样我们的全局异常处理就可以捕获到。
在application.yml配置文件增加以下配置项:
# 当HTTP状态码为4xx时直接抛出异常
spring:
mvc:
throw-exception-if-no-handler-found: true
# 关闭默认的静态资源路径映射
web:
resources:
add-mappings: false
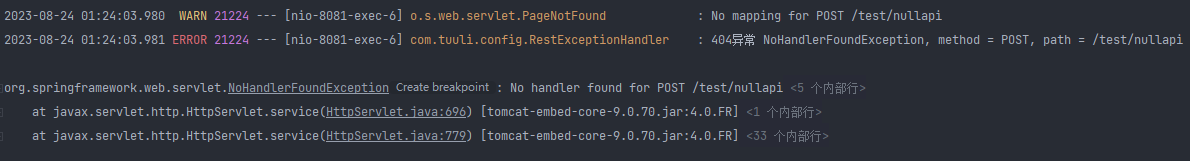
现在当我们再次请求一个不存在的接口是,控制台会报NoHandlerFoundException异常,然后被全局异常处理捕获到并统一返回
返回json:
{
"code": 500,
"msg": "操作失败,服务器繁忙或服务器错误,请稍后再试。",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692810621545
}
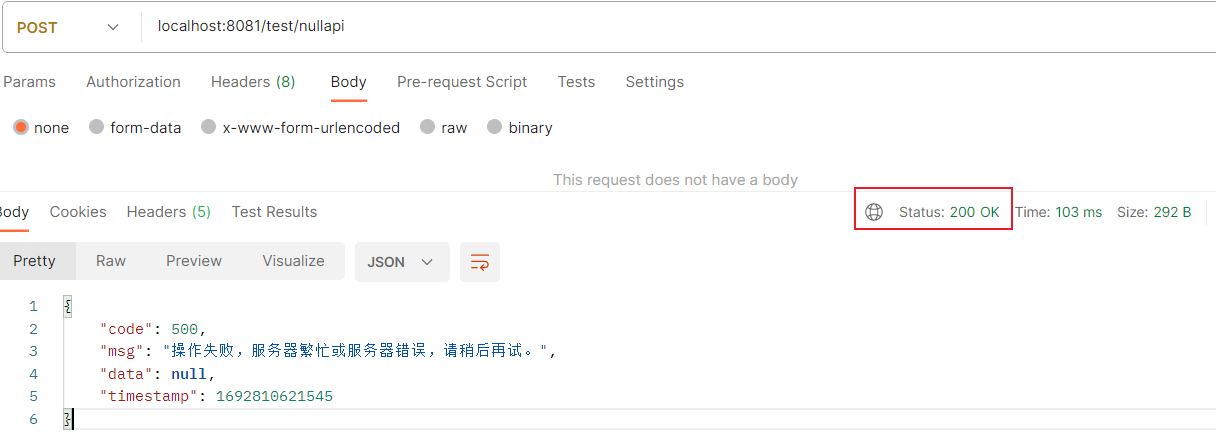
当发生404错误时,http的状态码依然是200,同时code返回的是500,这不利于用户或者前端人员的理解,因此我们可以在全局异常处理中单独对NoHandlerFoundException异常进行处理。
/**
* 处理404异常
*
* @param e NoHandlerFoundException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NoHandlerFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)//指定http状态码为404
public R<String> noHandlerFoundException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
log.error("404异常 NoHandlerFoundException, method = {}, path = {} ", req.getMethod(), req.getServletPath(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC404.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC404.getMsg());
}
在上面中,我们使用@ExceptionHandler(NoHandlerFoundException.class)单独捕获处理404异常,同时使用@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)指定http返回码为404,我们统一返回格式中code也设置为404
现在当我们再次发生404异常时,返回json如下:
{
"code": 404,
"msg": "未找到您请求的资源。",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692811047868
}

控制台日志:
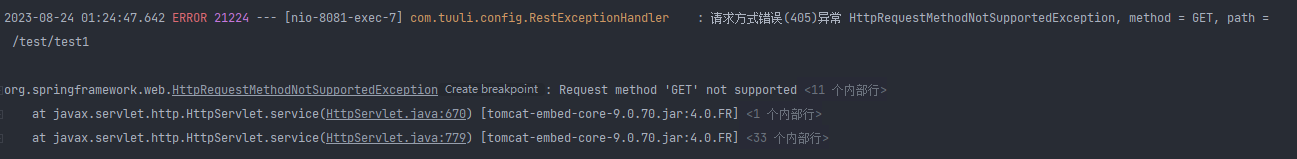
同理我们还可以为405错误进行配置,405错误对应的异常为HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
/**
* 处理请求方式错误(405)异常
*
* @param e HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED)//指定http状态码为405
public R<String> HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
log.error("请求方式错误(405)异常 HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException, method = {}, path = {}", req.getMethod(), req.getServletPath(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC405.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC405.getMsg());
}
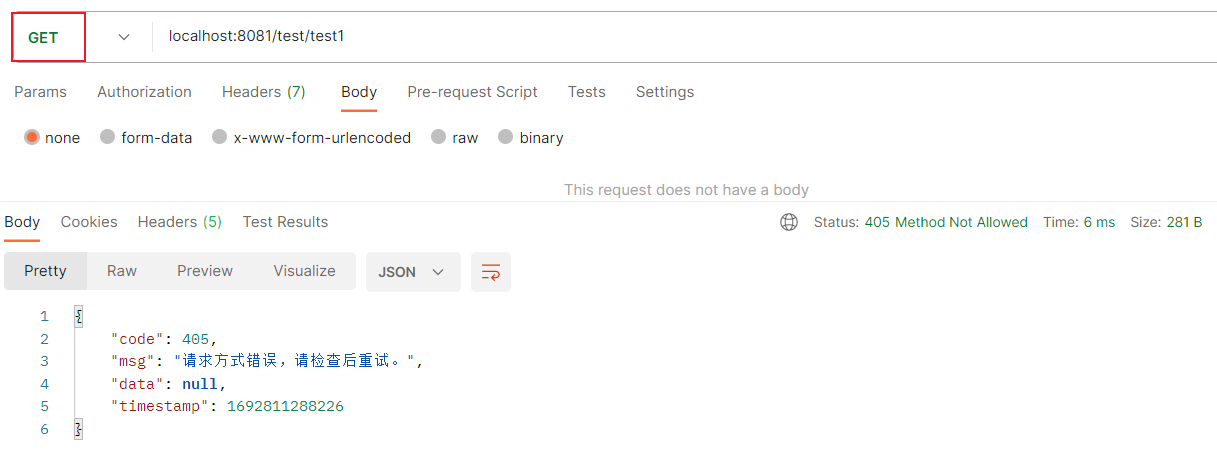
返回json:
{
"code": 405,
"msg": "请求方式错误,请检查后重试。",
"data": null,
"timestamp": 1692811288226
}
控制台日志:
全局异常处理RestExceptionHandler类完整代码如下:
package com.tuuli.config;
import com.tuuli.common.BusinessException;
import com.tuuli.common.R;
import com.tuuli.common.ReturnCode;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.NoHandlerFoundException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* 全局异常处理
*/
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class RestExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理自定义异常
*
* @param e BusinessException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public R<String> businessException(BusinessException e) {
log.error("业务异常 code={}, BusinessException = {}", e.getCode(), e.getMessage(), e);
return R.error(e.getCode(), e.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理空指针的异常
*
* @param e NullPointerException
* @return
* @description 空指针异常定义为前端传参错误,返回400
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = NullPointerException.class)
public R<String> nullPointerException(NullPointerException e) {
log.error("空指针异常 NullPointerException ", e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC400.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC400.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理404异常
*
* @param e NoHandlerFoundException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NoHandlerFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public R<String> noHandlerFoundException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
log.error("404异常 NoHandlerFoundException, method = {}, path = {} ", req.getMethod(), req.getServletPath(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC404.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC404.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理请求方式错误(405)异常
*
* @param e HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED)
public R<String> HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
log.error("请求方式错误(405)异常 HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException, method = {}, path = {}", req.getMethod(), req.getServletPath(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC405.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC405.getMsg());
}
/**
* 处理其他异常
*
* @param e otherException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public R<String> exception(Exception e) {
log.error("未知异常 exception = {}", e.getMessage(), e);
return R.error(ReturnCode.RC500.getCode(), ReturnCode.RC500.getMsg());
}
}
文章来源: 博客园
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!




 客服
客服


